
Undeniably an incredible technological innovation, 3D printing has taken the industrial world by storm, and car manufacturing is no exception.
By turning to 3D printing technology, the biggest car manufacturers in the world have built some of the finest pieces of machinery we’ve seen today, and we are more than excited to share them with you!
Below, you’ll find everything necessary to satisfy your curiosity in this still-elusive industry, and who knows – perhaps you’ll even discover your new favorite car.
Table of Contents
- Is it Possible to 3D Print a Car?
- How Does 3D Car Printing Work?
- What Type of 3D Printing Technology is Used to Print Cars?
- Other 3D Printing Technologies Used In Automotives
- What Materials Are Used To 3D Print Cars?
- Is there any Reason to Prefer 3D Printing in Car Building?
- Statistics on 3D Printing Automobile Industry
- The Best and Coolest 3D Printed Cars
- 1. The Blade (Divergent3D/Divergent Microfactories)
- 2. The Czinger 21C (Czinger Vehicles)
- 3. The Light Cocoon (EDAG)
- 4. Soulmate (EDAG)
- 5. 3D Printed Lamborghini Aventador
- 6. 3D Printed Parts for F1
- 7. The LSEV and XEV Yoyo (Polymaker/XEV)
- 8. LM3D (Local Motors)
- 9. The Lotus Type 62-2 and Lotus 340R
- 10. Nanyang Venture 8
- 11. The David Bowie Tribute Car (Takumi Yamamoto)
- 12. Auto Union Type C (Audi)
- 13. The Urbee (Kor Ecologic)
- 14. Micro Commuter (Honda Microcomputer and Kabuku)
- 15. The Shelby Cobra
- 16. The Olli 2.0
- Wrapping it Up
Is it Possible to 3D Print a Car?
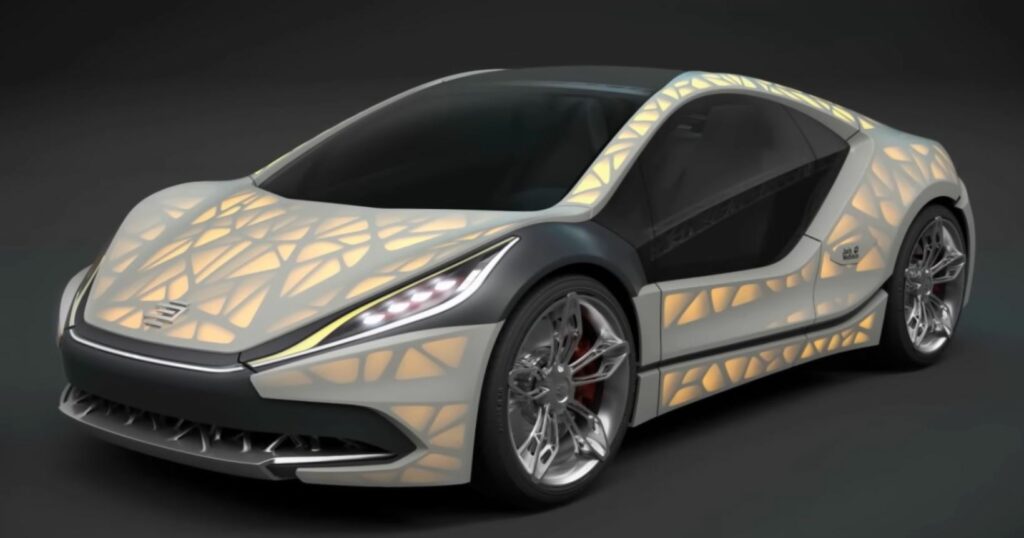

Certainly, and people are already doing it! However, printing cars isn’t as simple as feeding a model into a computer-generated 3D printer. There are a couple of extra steps to the process, and though sophisticated, may simplify future automotive production.
How Does 3D Car Printing Work?
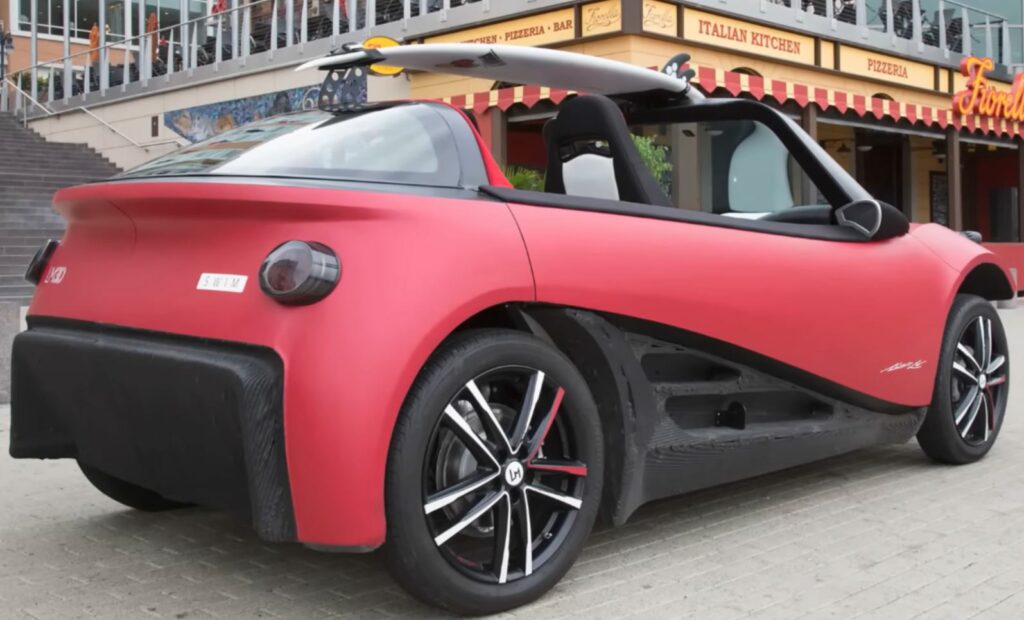

Most of us have heard many great things about 3D printing and how it works by now, yet 3D printing cars is still quite contemporary. Due to the complicated structure of our beloved wheeled machines (not to mention manufacturing material requirements), the process is more difficult than 3D printing a simple plastic toy or an architectural plan.
Now, one cannot simply print a full-scale 3D vehicle with the press of a single button – that is unless the entire production chain is automated and runs on the said button. But no, 3D printing automotive requires detailed design, precise printing of individual parts, and careful assembly.
First, manufacturers will use CAD software (or computer-aided design), sold either by the producer of the 3D printing hardware or by third parties. The CAD programs design individual parts of the cars and ensure that all the shapes, dimensions, and fits are in order.
Popular CAD software for the automotive industry includes Blender, Catia, and Solidworks, to mention a few. Furthermore, you can check out some free CAD files on grabcad.com if you’re curious to see what some basic 3D models look like.
Parts that are designed by CAD and 3D designers include everything from body exterior and panel parts to body interiors and trims, air and fluid handling parts (i.e., exhausts), energy and fuel management parts, the underhood, and all other necessary parts to construct a car. The part most often excluded is the car seats, steering wheel, and the like since leather cannot be 3D printed.
Next, parts need to be individually 3D printed by industrial-grade 3D printers. Additive manufacturing is extremely precise, and your machinery is in good condition as long as your designs are planned well. If you have enough of the required material, the parts should be perfectly identical each time.
The top players manufacturing 3D printing equipment for the automobile market include:
- 3D Systems Corporation
- Desktop Metal Inc.
- General Electric Company
- Sinterit
Among many others. It’s still a rather new industry, so you’re sure to expect many new and old players to join this list.
Most companies in this field have machines with different focal points in the production line. Some are more concerned with quickly creating simple parts, while others are better at computing intricate CAD files. It is recommended that those interested in acquiring their printers seek out the company and request a consultation.
Finally, we reach the assembly step. If it had not yet been clear, 3D printed cars are made using a modular assembly system where parts are individually made and then pieced together until we reach the end product – much like the production philosophy (assembly line) of Henry Ford! The modular approach allows for better quality control since if one part is faulty, you need to replace that.
What Type of 3D Printing Technology is Used to Print Cars?
Not all 3D printing functions in the same fashion; naturally, they are more equipped for certain purposes. Comparative advantages and scale are everything when you want to streamline your production line; therefore, the need for different 3D printers is clear. Generally, three types of 3D printing are primarily used in the automobile industry:
FDM
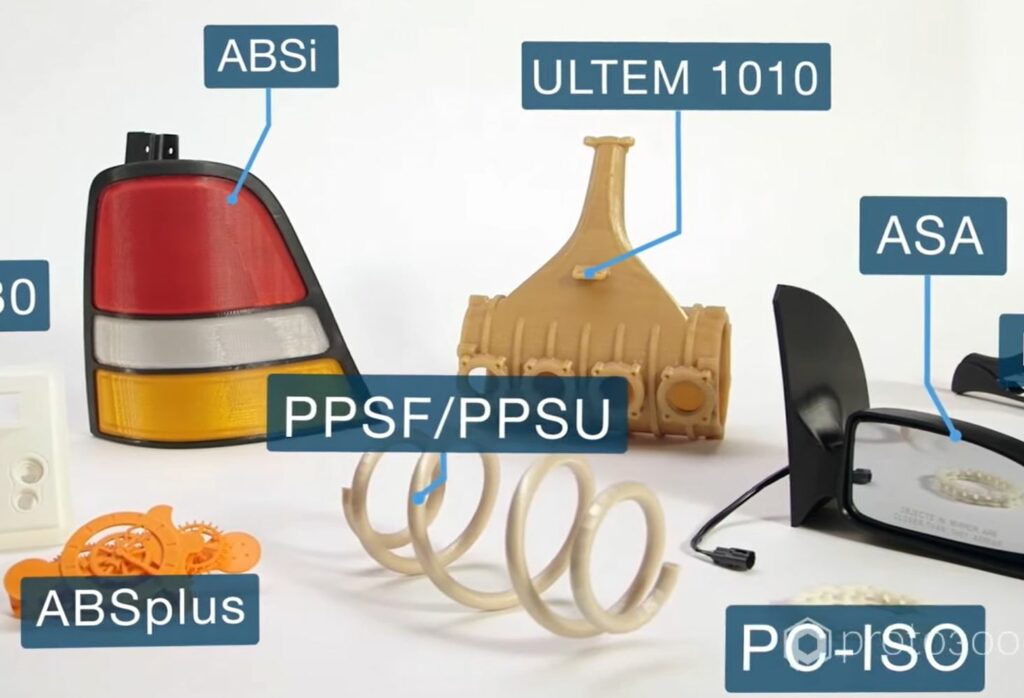
FDM, or fused deposition modeling, is the layering of filaments of thermoplastics or other materials according to a 3D image or CAD file’s pattern. With FDM, the nozzle moves along the horizontal plane (X and Y axes) over a build platform. This platform then moves up and down according to the requirements of the CAD pattern to introduce the Z axis to the 3D print.
SLA
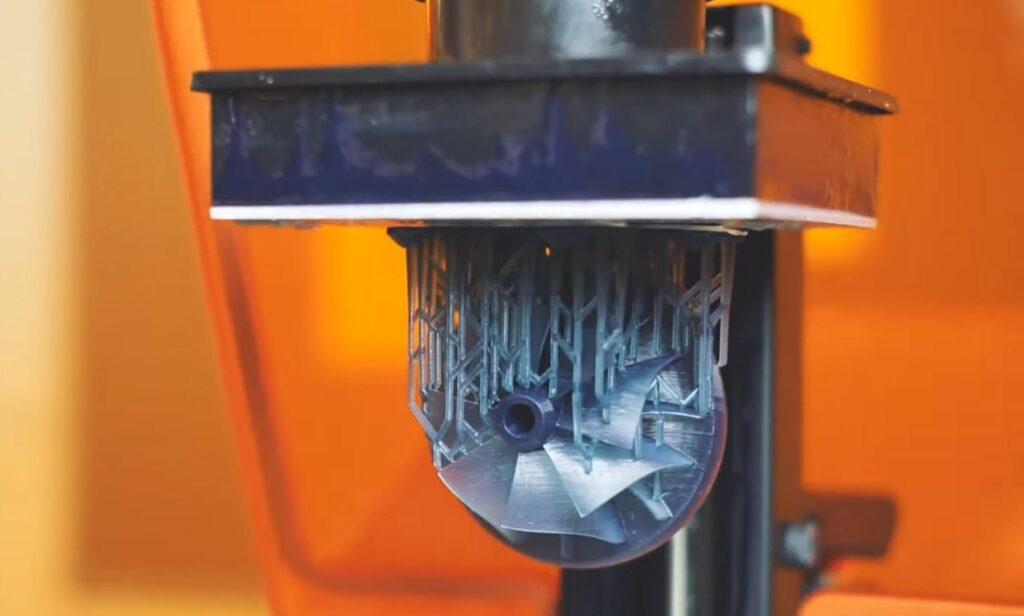

Stereolithography (SLA) includes using a laser to create an object out of resin layers. SLA is efficient in creating specialized parts that require high detail and accuracy and has extremely small features, as tiny as one-fiftieth of an inch (0.07mm). It is often employed to produce tiny interior accessories, full-sized panels, door handles, cast metal brackets, lights, or low-volume parts.
SLS
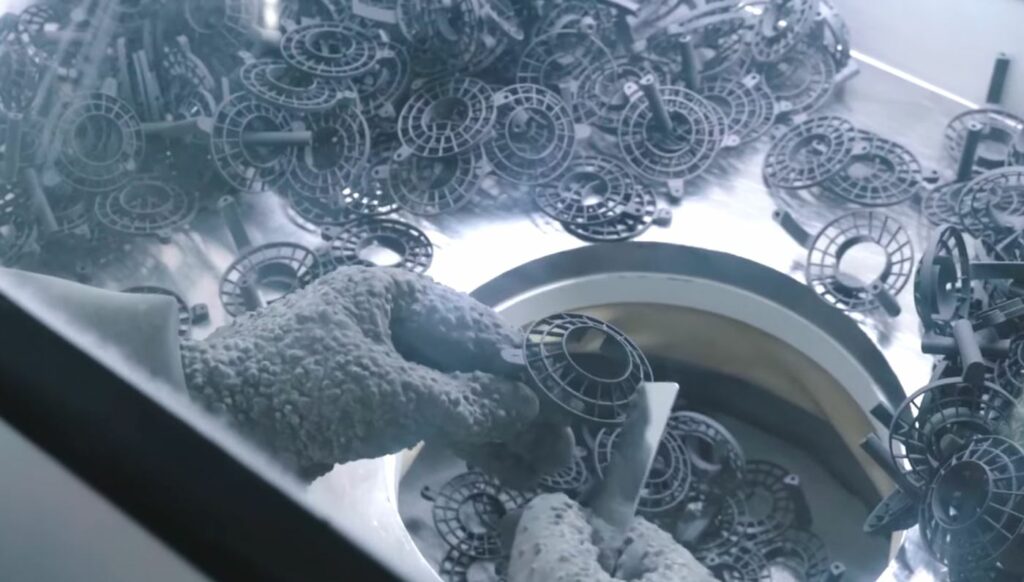

SLS stands for select laser sintering, which (as the name implies) uses a laser to fuse small particles of various materials (either plastic, metal, glass, etc.) into the desired three-dimensional shape. SLS is useful in producing complex functional parts, especially those with hollow internal structures, and is also used to hollow out unnecessary materials in otherwise heavy parts, allowing the car’s weight to be less.
Other 3D Printing Technologies Used In Automotives
Metal 3D printing uses a laser to combine layers of metal with complex geometries and is used to print car parts as (similar to SLS) it allows the production of sturdy parts with low weight-to-strength ratios. The last tech used in the industry is carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) 3D printing, using various processes to print objects with a fibrous matrix.
What Materials Are Used To 3D Print Cars?
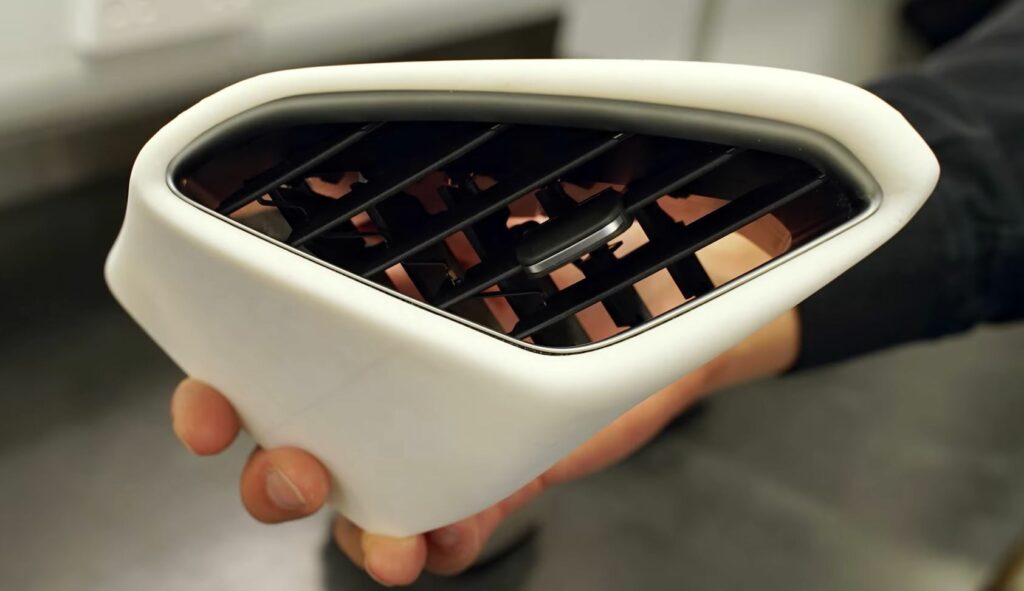

There are many options of materials that are used for 3D printing automobile parts. Part of the design process entails engineers weighing the cost/benefit and various pros and cons between different materials for different parts before deciding on a final material or combination thereof. Generally, car parts are 3D printed using plastics, metals, composites, resin, or a combination thereof.
Is there any Reason to Prefer 3D Printing in Car Building?
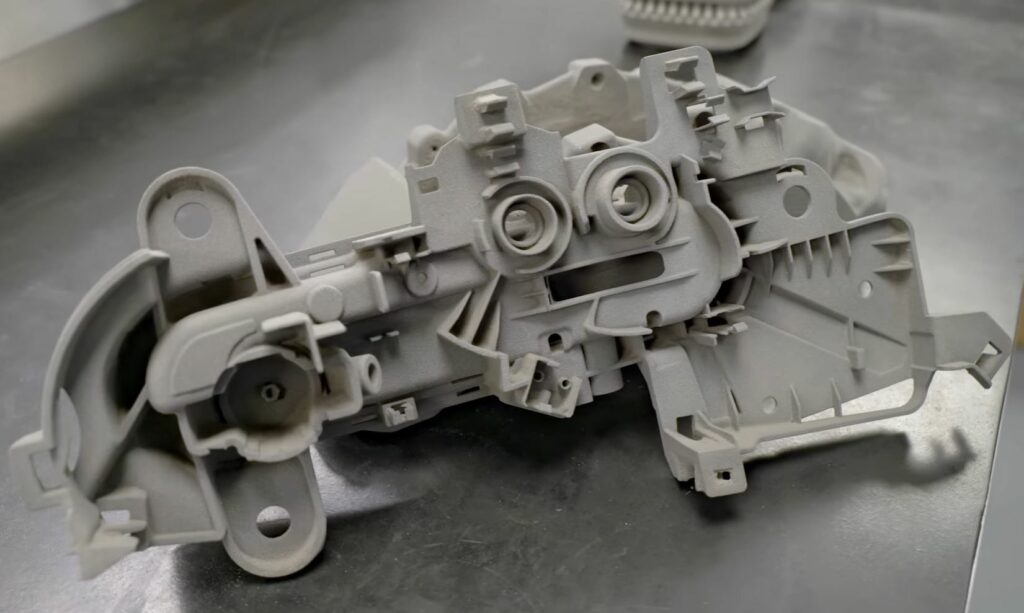
3D printing vehicles have introduced an array of improved efficiencies in contrast to the assembly line. There are, however, certain limitations, and the technology is not useful in all stages of the creation of a vehicle. Let’s consider some pros and cons of 3D printing an automobile.
Benefits of 3D Printing a Car:
- Design changes can happen at any stage.
- It allows for rapid prototyping.
- Waste is minimized, and recycling is promoted.
- Printing on demand is possible if the process is fast enough to meet the delivery.
- Allows a more lightweight design.
- Uses fewer materials than conventional methods.
Drawbacks to 3D Printing a Car:
- Limited options of materials.
- The size of structures cannot always fit under machines.
- Design inaccuracies can be wasteful.
- Lots of post-processing is required.
Statistics on 3D Printing Automobile Industry
The world’s 3D printing automobile industry is expected to grow by 23.69% over FY2022 to reach a WHOPPING $2.34 BILLION by the end of the year. Analysts expect the growth rate to continue at the same pace for the near future (around 5 years) due to the fast pace at which R&D is happening, and new entrants continue to join the market!
Furthermore, the industry complements the already established and rapidly expanding EV industry. Another bonus propelling the lucrative industry is that it is fundamentally environmentally beneficial, as recyclable materials are used in production.
The Best and Coolest 3D Printed Cars
3D printed cars will surely disrupt the automobile industry in ways that will inspire even more innovation, efficiency, and safety. 3D printed cars will not only become better, lighter, faster, and more environmentally friendly, but they are also becoming cooler. The technology is pushing the boundaries of car design where previously impossible shapes and features are now all within reach.
1. The Blade (Divergent3D/Divergent Microfactories)
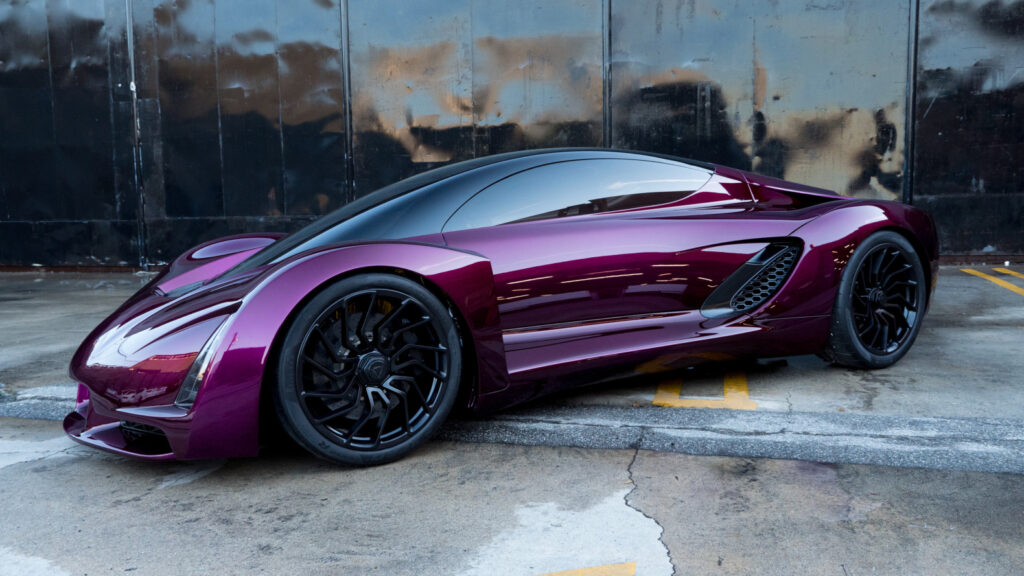

This car screams, “the future is now.” The car’s exterior is as sleek and sharp looking as its name suggests; the Blade is the 3D printing world’s first hypercar baby. The entire chassis of the Blade was made through additive manufacturing, and it is a whopping 90% lighter than those of traditionally manufactured supercars, yet is equally as strong, if not stronger.
Designed by Kevin Czinger and Divergent Technologies, the Blade was fully printed and assembled in California and weighed a mere 1,389 lb. Although never released to the public, the Blade served as the face of the 3D startup (Divergent). It helped create interest in possible investors and raised funds which led to the company’s later production of cars, which brings us to the second item on this list.
2. The Czinger 21C (Czinger Vehicles)
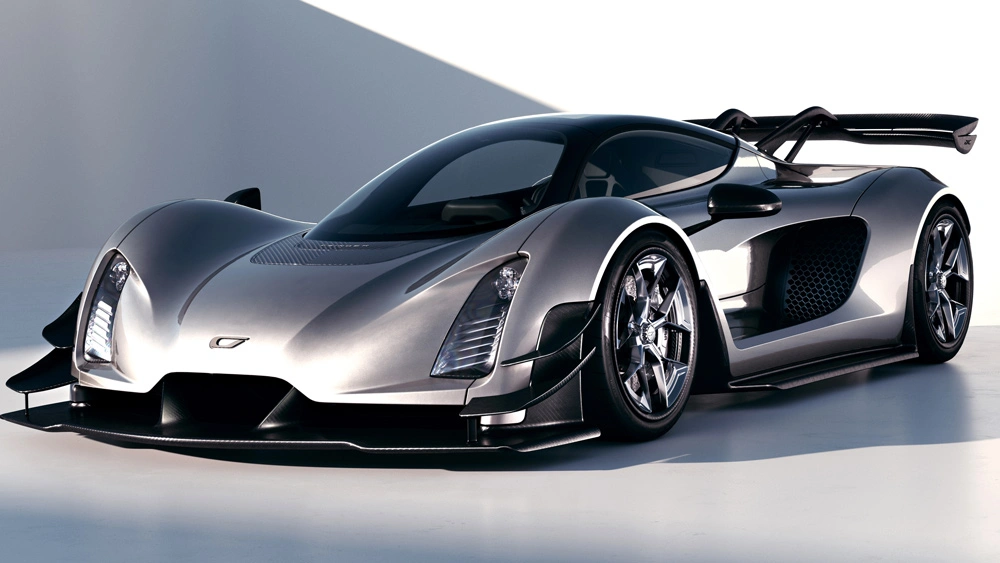

Inspired by (or rather, a derivative of) the Blade, the Czinger 21C was developed by a collaboration between Divergent3D and Czinger vehicles. The Czinger 21C is the company’s first production car and flagship. Czinger Vehicles expects to start deliveries of these supercars in the first quarter of 2023, limiting their production to only 80 units.
A 2-door coupé featuring an impressive powertrain, the Czinger 21C has 1,250 horsepower. It is almost double the weight of its predecessor, weighing about 2760 lb. The legacy of these two cars doesn’t just stop there, though, as they inspired the creation of an array of other models, including the Czinger 21V Max and the Czinger Hyper GT.
3. The Light Cocoon (EDAG)
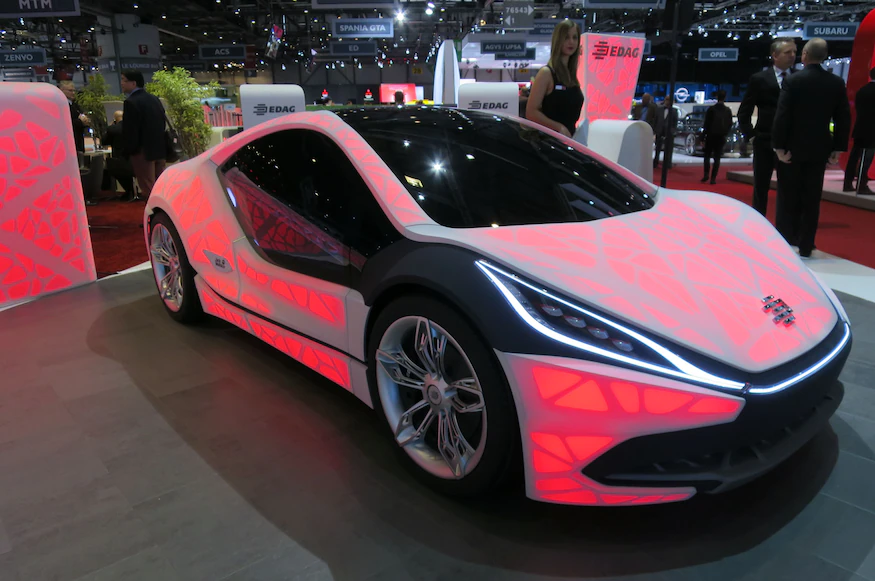

Now continuing on the trend of 3D supercars, EDAG’s Light Cocoon concept car is a superb example of how additive manufacturing technology is changing the automobile industry. The body has an extremely sleek design, and looking at it feels like one is catching a glimpse of the future – because that’s what we’re looking at
Only the body itself is 3D printed, but that is no reason not to include it in the list, especially when considering how impressive it is. Due to the naturalistic design, almost imitating branches and leaves, the Light Cocoon is extremely lightweight, and is produced using mostly polymer and other composites.
4. Soulmate (EDAG)
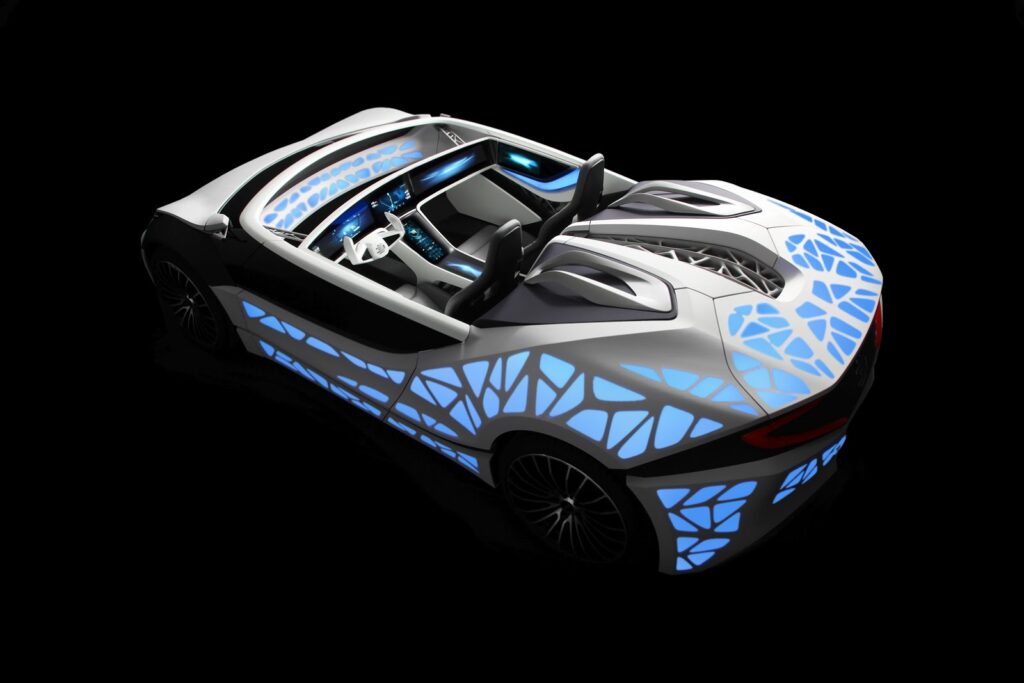

Another car brought to life by EDAG is Soulmate. Created through select laser sintering printing, the Soulmate similarly derives its body’s iconic look from nature. This concept car’s internet connectivity and smartphone app integration make it unique. Similar to how many people live in “smart homes,” EDAG’s goal with Soulmate is to create a smart car.
In addition, the car’s smart features can be controlled simply using gestures and visual signals to ensure that drivers are not operating it irresponsibly. Another key feature of the model is autonomous driving, further enhancing the car’s smart capabilities.
5. 3D Printed Lamborghini Aventador
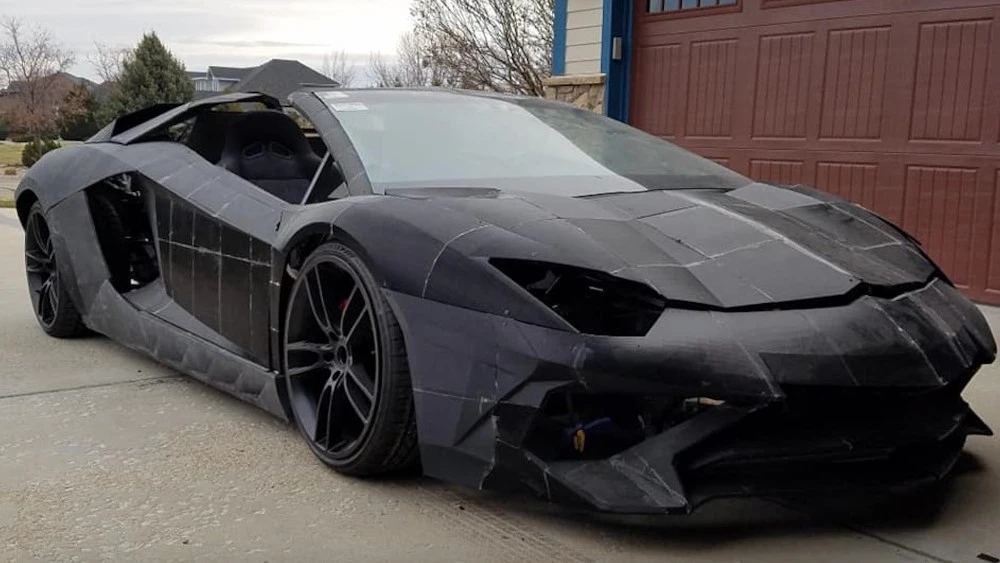

This one is a little different from the rest – the 3D printed Lamborghini Aventador was all made and assembled in a Colorado family’s garage as a project the father and his young boy undertook. All except for parts such as the windows, the engine, and other parts are impossible by 3D printing.
What’s amazing about the car is that it shows how groundbreaking the technology is. As long as you have the will, enough data on the desired model (or enough creativity to design your own), you can fully 3D print your car.
6. 3D Printed Parts for F1
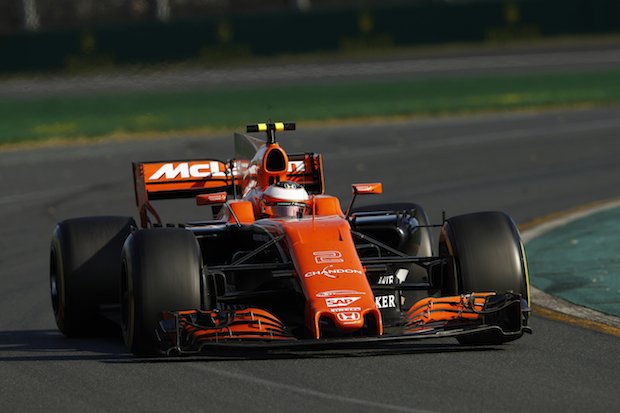

Though strictly speaking, not a 3D printed car, McLaren recently started employing 3D printing to manufacture some of their parts. Since the Covid-19 crisis brought tremendous problems to the high-speed racing industry, mostly in the form of revenue shocks, the team budget has been reduced dramatically.
McLaren responded to this issue by starting to pioneer 3D printed car parts to reduce costs. Furthermore, McLaren can reduce their carbon footprint due to reduced environmental costs associated with transporting the parts that are now made in-house.
Additive manufacturing also allows car makers to experiment more liberally with different shapes and designs to reduce weight, increase aerodynamic efficiency, and make the car go faster. It is unclear how far 3D printing will go in the sport, but you can expect to hear much more about 3D printing from F1 enthusiasts and insiders soon.
7. The LSEV and XEV Yoyo (Polymaker/XEV)
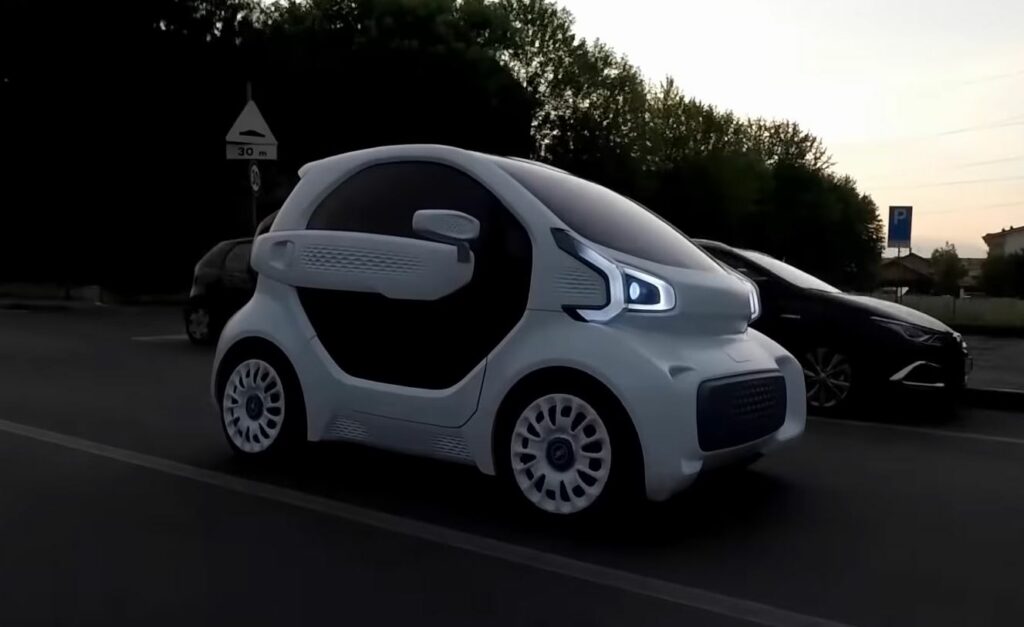

A collaborative effort by Italian/Hong-Kong based car company XEV and 3D printing experts Polymaker, the LSEV is the world’s first 3D printed electric vehicle to go into full mass production. Combining two groundbreaking technologies, the LSEV is perhaps a staple of what the future of the automotive industry could look like, giving us a glimpse into the (near) future of our urban centers’ roads.
Though compact cars are not always appealing to those who want a cool-looking ride, their efficiency and cost-effectiveness cannot be overlooked. Eventually, the concept car gained popularity, and the name changed to the XEV Yoyo upon production. The body of the LSEV, including the interior, is 3D printed and designed modularly to increase production efficiency.
The 3D printed parts of the vehicle are made with enhanced nylon, polylactic acid, and thermoplastic polyurethane. With a 150 km range for each charge and weighing only 882 lb, the XEV Yoyo is a clear competitor for established compact cars, such as the Smart car.
8. LM3D (Local Motors)
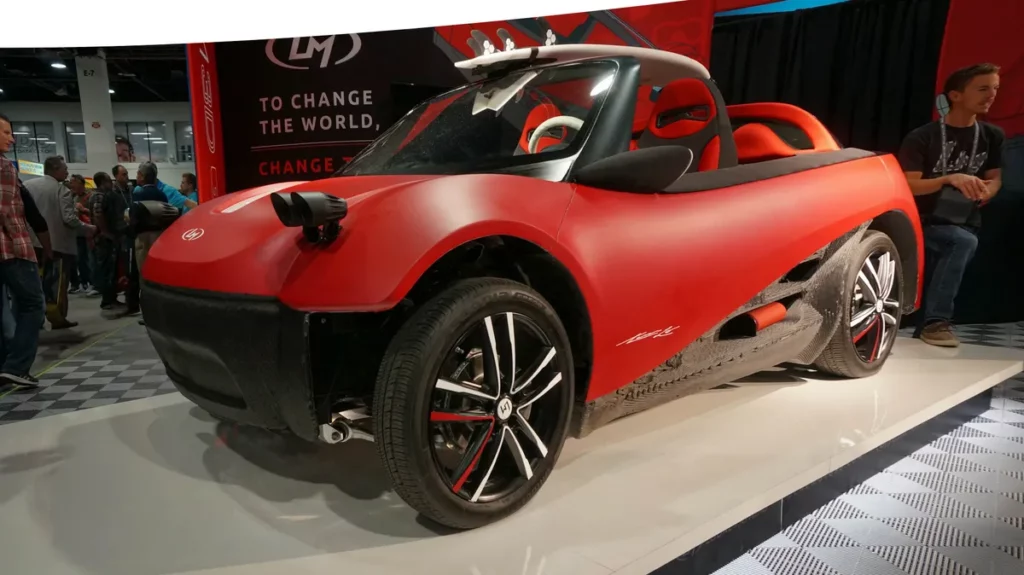

Local motors drew inspiration from their previous model, the Strati, to develop the next generation in their 3D printed cars. Consisting of only 49 parts, the LM3D is 75% 3D printed, and its printed parts consist of 80% recycled plastics and 20% carbon fiber. Most impressive, the LM3D took only 2 months (from design to final product) to make its prototype.
9. The Lotus Type 62-2 and Lotus 340R
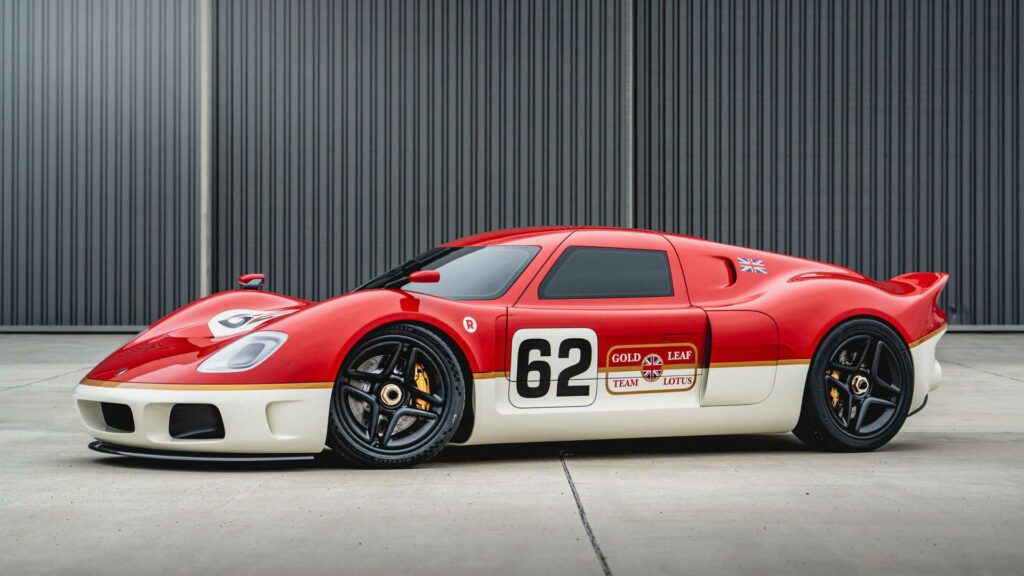

Vintage car enthusiasts will be happy to hear that 3D printing allows us to enjoy more cost-efficient and environmentally friendly products and brings the resurrection of vintage and limited edition models that have gone out of production. That’s right, your favorite cars from old movies, dramatic races, and all the like can be accurately reproduced by 3D printing.
There are no better examples of this revival than the Lotus Type 62-2 and the Lotus 340R. CIDEAS employed additive manufacturing to reconstruct the Lotus 340R from scratch, using 3D scans taken of the original model to get the necessary CAD files. Furthermore, you can catch a glimpse into Ant Anstead and Jenson Button’s project of rebuilding the Lotus Type 62-2 on Discovery+.
10. Nanyang Venture 8
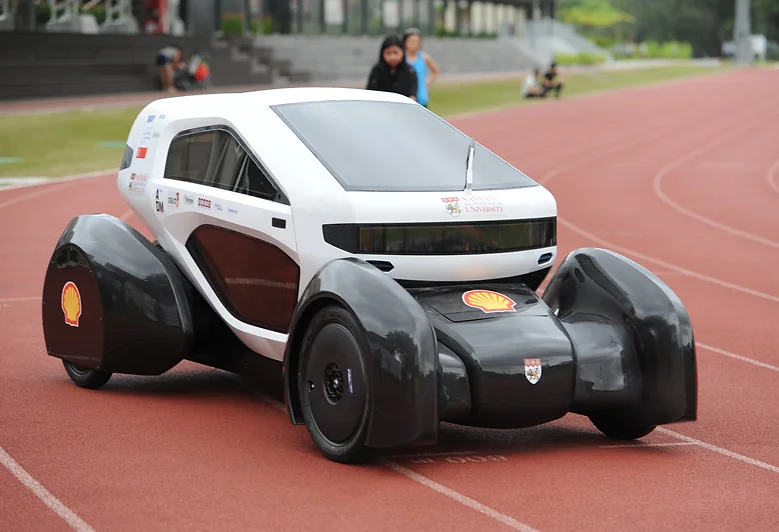

The Nanyang Venture 8 is a special example of the potential of 3D printed automobiles, designed and produced in only 3 months. The car is the final product of university students at Nanyang Technological University under the guidance of prof Ng Heong Wah. For their entry in the 2015 Shell Eco-Marathon, the Nanyang Venture 8 claimed first prize.
An interesting concept of the car is that customers should be able to fully customize the driver’s cabin, i.e., change the shape, color, and other aesthetics to suit their preferences. Additionally, the car is powered by lithium-ion batteries, rechargeable by solar panels on the cabin’s roof.
11. The David Bowie Tribute Car (Takumi Yamamoto)
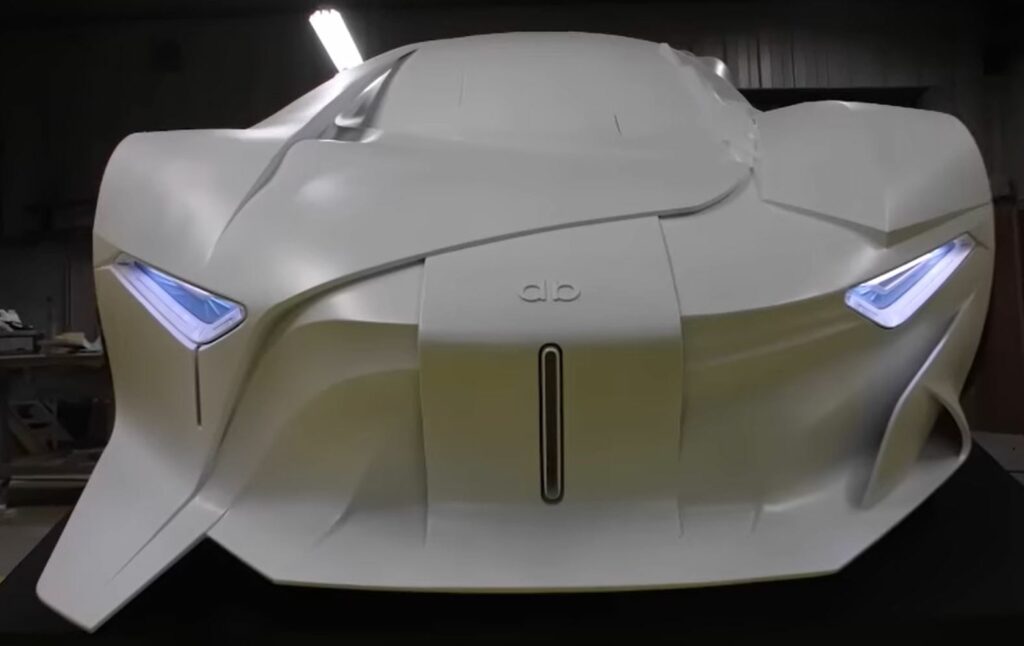

Takumi Yamamoto, the designer of Citroen’s GT, has always been fascinated with the late rock legend David Bowie. Yearning to start some collaborative effort with the artist, he was inspired to design the “db” concept car upon hearing that Bowie had passed away.
Certainly a very daring and eccentric design, the car captures the essence of Bowie’s imaginative dream: influencing artistic movements, taking risks, and breaking frontiers. Yamamoto adds that he was impressed by how quickly they could print the design.
12. Auto Union Type C (Audi)
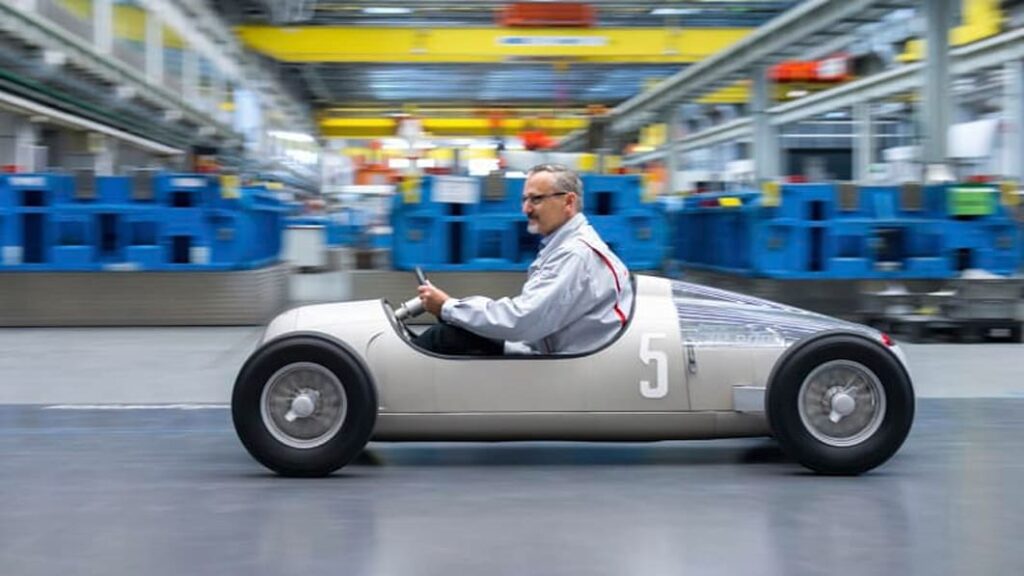

Audi is also trying to establish itself as a pioneer in this new industry. Most remarkable is their reproduction of a Type C racer from the 1930s. Using original design prints from the Auto Union, Audi created a replica using aluminum and metal alloys created by 3D printing.
13. The Urbee (Kor Ecologic)
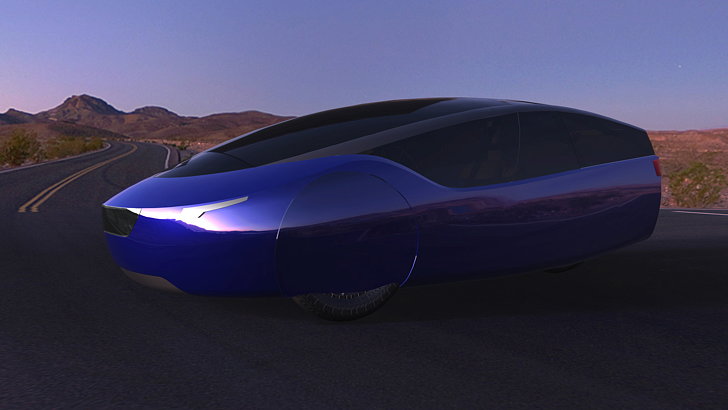

Many companies in the automobile industry that are interested in 3D printing technology have an equal passion for the environment. As their name suggests, Kor Ecologic is no exception, and the Urbee – the greenest automobile in the world – is their proof.
The Urbee is a collaborative effort with Stratasys, and the car is built using FMD 3D printing technology. What’s most impressive about the car is that it can run from San Francisco to New York on a mere 10 liters of ethanol and weighs only 1200 lb!
14. Micro Commuter (Honda Microcomputer and Kabuku)
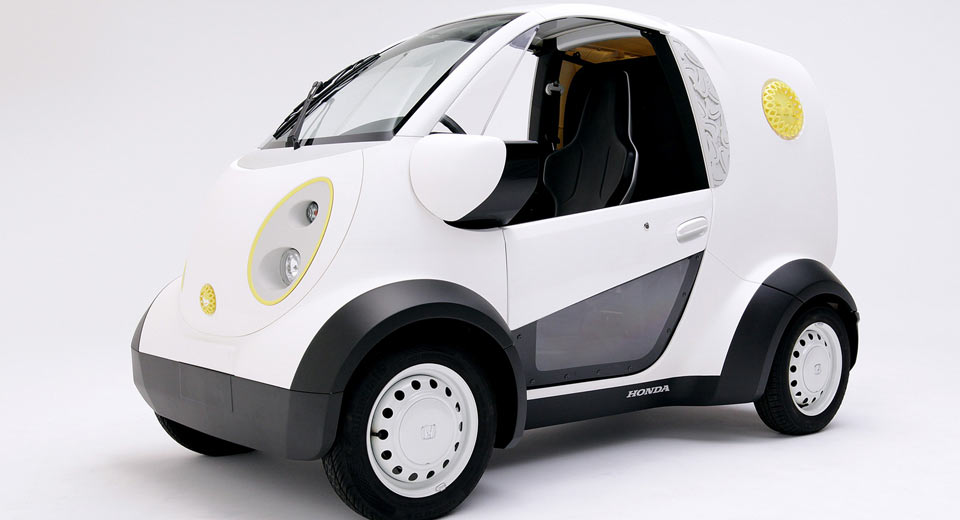

Honda collaborated with the Japanese 3D printing startup, Kabukum, which is focused on CAD software. They printed the car within 2 months, and only the chassis and powertrain were not printed. The vehicle allows for a 50-mile range and was designed as a small delivery vehicle for a popular Japanese cookie manufacturer.
15. The Shelby Cobra
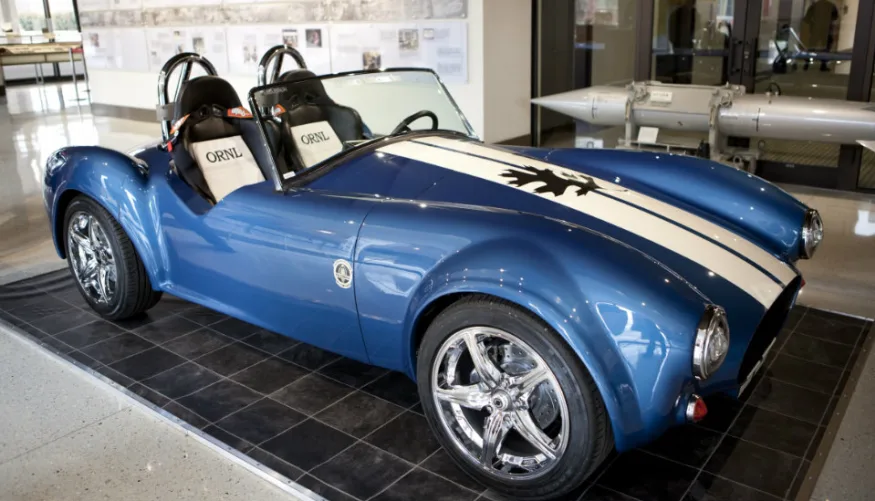

There are few models as iconic as the blue and white-striped Shelby Cobra. It’s no wonder car enthusiasts want to see this car come back to life in its 3D printed glory. The car was 75% 3D printed, and it only took 24 hours! Currently, the vehicle is employed as the ambassador for 3D printing automobiles in the US, traveling the country and attending various events to promote the tech.
16. The Olli 2.0
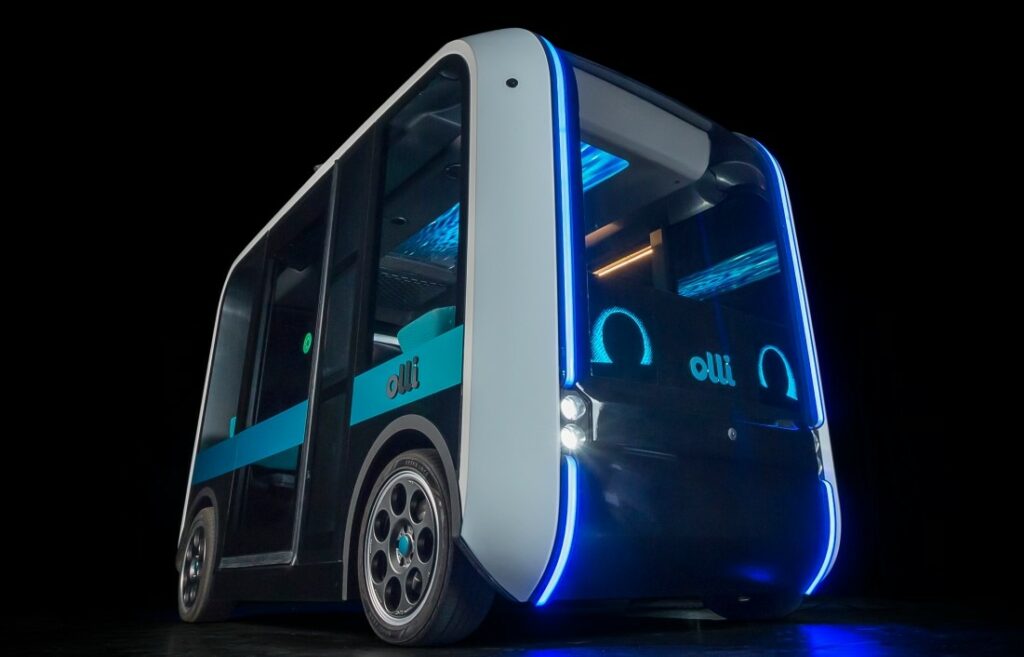

The final feature on our list of the best/coolest 3D printed cars is not a car. Rather, it is a 3D printed bus, all made by Local Motors. In this case, unlike most, the entire chassis of the bus is 3D printed. Certainly, it is a remarkable feat considering the importance of a sturdy and stable chassis for vehicle safety, comfort, and general working.
The Olli 2.0 is Local Motors’ first production vehicle and has all the features one would expect our future public transport to have. It is electric, self-driving, and completely connected (network/internet-wise). Ollis has already been deployed to a couple of urban centers worldwide.
Wrapping it Up
Are you as excited about the future of additive manufacturing as we are? It is crazy to think that this once elusive technology has now become a staple of pioneering in engineering.
As the benefits and adoption of 3D printing continue to soar in the automobile industry, additive technology will surely continue to transform the way vehicles are designed, built, and maintained around the world. Don’t miss out on the fun, start your 3D printed car project today!


