On any FDM 3D printer, the extruder is one of the most essential components, responsible for pushing filament into the hot end. But not all extruders are the same, and there are two main types of extruder configurations on FDM 3D printers: Bowden and Direct Drive.
A Bowden setup comprises an extruder assembly that’s separated from the printhead (hot end), with a tube (known as a PTFE tube) going between the two entities for filament to go through. On the other hand, a direct drive extruder configuration has the extruder assembly attached to the printhead, where it’s directly above the hot end (minimal PTFE tubing required).
And, while the fundamental goal of each extruder configuration is the same, they offer different benefits. For instance, Bowden extruders are less expensive and allow for faster print speeds. Direct drive extruders cost a bit more than their alternative but can print flexible filaments (e.g. TPU) better and offer more precise filament extrusion.
Want to hear more about the differences between Bowden and direct drive extruders? Well, just keep reading!
Table of Contents
What is a 3D Printer Extruder?

A 3D printer extruder is a sub-assembly of an FDM 3D printer, made up of a stepper motor and a set of drive gears. The purpose of the extruder assembly is to push the inserted filament through the hot end and out the nozzle, so it can be laid out on the print space to form your desired 3D model. As such, an extruder is needed in any FDM 3D printer; without one, filament wouldn’t flow!
So how does a 3D printer extruder work? Well, it’s pretty simple!
Filament is inserted from one end of the extruder assembly and goes in between two rotating gears. Typically, only one of these rotating gears is considered the “drive gear”, which is the studded gear that actually pushes filament. The other gear on the extruder assembly (unless it’s a dual-drive extruder) is a non-studded bearing, known as the “idle gear”, which rotates freely when the drive gear pushes filament.
The drive gear is connected, in some way, to the axle of the extruder stepper motor. So when the motor axle rotates, so does the drive gear, pushing filament in one direction.
Where the filament goes after being pushed by the extruder differs based on the extruder configuration.
What is Bowden Drive?
Bowden drive is an extruder configuration where the extruder assembly, including the stepper motor and gear mechanism, is separated from the hot end of your 3D printer. A long PTFE tube connects one end of the extruder assembly to the top of the hot end on the printhead, so filament can flow in a controlled manner between these two entities.
Moreover, when the filament is pushed out of the extruder assembly, it goes past the PTFE coupler, through the PTFE tube, and into the hot end. For reference, the PTFE coupler is the part that screws into the outflow end of the extruder assembly and holds the Bowden tube in place. There’s also a PTFE coupler on the top of the hot end assembly.
Typically, the extruder assembly on a Bowden extruder 3D printer is placed on the X-axis gantry of the 3D printer, such as in the case of Creality Ender 3 V2 and the Prusa Mini+. However, sometimes the extruder is mounted to the side of the printer’s frame, like on the Creality Ender 5 Pro.
Advantages of Bowden Extruders
Below, I’ve gone over the main advantages of Bowden extruders in the form of bullet points:
- Less Expensive: Most Bowden extruders are less expensive than direct drive extruders. This is mostly because Bowden extruders don’t have as compact of an assembly as direct drive extruders, so manufacturers don’t need to spend as much time building the extruder (which lowers the cost).
- Easier to Fix: Going off of the last point, because Bowden extruder setups are separated from the hot end and aren’t super compact, they are also usually easier to fix for users. This is especially helpful for those new to the 3D printing space.
- Faster Print Speeds: Because the printhead assembly on a Bowden extruder 3D printer doesn’t have to hold the extruder assembly, it’s very lightweight. And, with a lightweight printhead, higher print speeds are achievable without a drop in the quality of prints.
- Less Ringing: Ringing is a specific print quality issue where vibrations, typically caused by a heavy printhead, lead to visual distortions on the outer surface of 3D prints. Because the printhead on a Bowden-drive 3D printer is lighter than a direct-drive printhead, there will be less ringing on prints.
Best Bowden Extruders
If you’re interested in getting a Bowden extruder, check out these products below. I’ve provided both standalone Bowden-drive extruders as well as printers that come, in their stock form, with a Bowden-drive extruder.
Extruders
3D Printers (Bowden)
- Creality Ender 3 V2 (as well as the Original and Pro versions)
- Prusa Mini+
- Anycubic Kobra Max (and Kobra Plus)
- Anycubic Kobra Go
- Creality CR-10
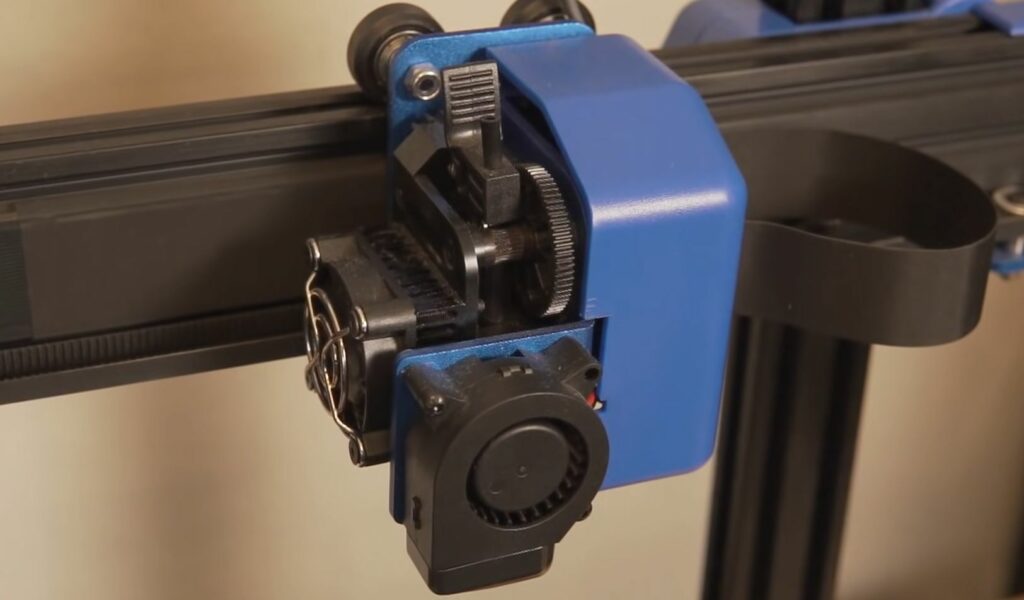
What is Direct Drive?
Direct drive, the alternative to Bowden drive, is an extruder configuration where the extruder assembly is directly above the hot end. This means the entire extruder assembly is attached to the printhead, rather than mounted to the frame or X-axis gantry of the printer.
Because there is only a very small gap between the outflow end of the extruder and the top of the hot end, a long Bowden tube isn’t used on direct drive extruder setups. However, it’s important to note that some DIY direct extruder configurations use a small length of Bowden tube. Still, it’s nowhere near as long as the PTFE tube that’s used on Bowden-drive printers.
Traditionally, direct drive extruders were only found on higher-end 3D printers, like machines made from Ultimaker, LulzBot, and other top-notch 3D printer brands. However, due to the rise of budget 3D printer companies, direct-drive 3D printers are becoming just as affordable as Bowden-drive machines. Examples of direct drive 3D printers include the Creality Ender 3 S1, Elegoo Neptune 3 Plus, and the Prusa i3 MK3S+.
Advantages of Direct Drive Extruders
Below, I’ve gone over the main advantages of direct drive extruders in the form of bullet points:
- Improved Extrusion Precision: Because direct drive extruders use only a small length of PTFE tube, there is less slack in the filament line. This makes direct drive extruders a lot more precise regarding filament extrusion than Bowden extruders. Because of this, problems such as over and under-extrusion are less common on direct drive 3D printers.
- Improved Reliability: Similar to the last point, because there is a much smaller gap between the extruder and hot end, there is less space for filament to jam. As such, direct drive extruders offer improved reliability over Bowden extruders.
- Lower Retraction Settings: Direct drive extruders require lower and less-intensive retraction settings than Bowden-drive extruders. This means you can set a lower retraction distance and retraction speed in your 3D slicer, without having to worry about stringing on your prints.
- Improved Print Quality for Flexible Filaments: Due to the improved extrusion precision as well as the minimal use of PTFE tubing, direct drive extruders can print flexible filament materials, such as TPU and TPE, better than a Bowden extruder can.
- Lower Motor Power Requirements: You can get away with using a lower-power extruder motor on a direct drive extruder setup than you can with a Bowden extruder. This is because direct-drive extruder setups don’t use a long PTFE tube, so the direct-drive extruder doesn’t need as much torque to push filament through the hot end as a Bowden-configured extruder.
Best Direct Drive Extruders
If you’re interested in getting a direct drive extruder, check out these products below. I’ve provided both standalone direct drive extruders as well as printers that come, in their stock form, with a direct drive extruder.
Extruders
3D Printers (Direct Drive)
Can I Print TPU with a Bowden Extruder?
Yes. Your prints just won’t be super high-quality.
Printing flexible filament materials, such as TPU and TPE, is technically possible on printers with a Bowden extruder. However, it’s not recommended because, as I’ve mentioned, Bowden printers struggle with printing these materials due to their elasticity.
When you load TPU filament into your Bowden extruder setup, the extruder is pushing the filament through the entire PTFE tube and into the hot end. Inside the PTFE tube, the flexible material is more likely to tangle, bind, and stretch, which causes problems with the printer’s extrusion and can even lead to full-on hot end clogs.
Because of this, typically, TPU 3D prints made on Bowden-drive 3D printers are of much lower quality than those made with a direct-drive machine. But, if you’re okay with a drop in print quality and can live with a higher risk of print failures, then go right ahead and load some NinjaFlex into your printer’s Bowden extruder!
Conclusion
Overall, both Bowden and direct drive extruders are great options for any FDM 3D printer. But they work slightly differently, making each system slightly better for different applications.
If you’re just getting into 3D printing and want a low-cost, easily-fixable extruder, I strongly recommend going with a Bowden extruder (or a printer with a Bowden extruder). These extruders don’t handle flexible materials well but are super easy to use when printing basic materials, like PLA, ABS, and PETG. Plus, a Bowden extruder can handle faster print speeds than direct drive extruders.
On this note, I suggest going with a direct drive extruder if you want to print flexible filament materials, like TPU or TPE, as this extruder configuration won’t jam when printing these materials. Additionally, direct drive extruders are more precise in their filament extrusion, so you can expect fewer over and under-extrusion issues with this extruder setup.
But, no matter your choice, both are great options, and I hope you can achieve high-quality prints!

