
With its excellent strength-to-density ratio and lightweight feel, HDPE filament quickly established itself as a go-to solution for 3D printing. Plus, this material is recyclable!
If you’re in the market for a new type of filament for your next 3D printing project, HDPE or High-Density Polyethylene could be an exciting material. However, this material isn’t as popular as it once was. Still, it’s essential to consider the drawbacks that caused other materials to replace HDPE.
Table of Contents
What Is HDPE Filament?

HDPE is short for High-Density Polyethylene. While this name sounds like a mouthful, it’s a subcategory of Polyethylene (PE), a member of the critical family of polyolefin resin, which is the most widely used plastic in the world.
Polyethylene has become the most widely used plastic globally thanks to its low cost. It’s also a material that resists humidity well and is easy to work with, thanks to its flexibility. Plus, polyethylene can withstand heat, chemicals, and impact forces.
Another advantage is that polyethylene is recyclable as long as the material is clean and dry.
Polyethylene has other interesting properties, such as the ability to adopt linear or branched molecular structures that cause the material’s density to vary. HDPE, or High-Density Polyethylene, has a thickness of 0.941 g/cm3 or higher.
HDPE is a popular 3D printing material for objects that require resistance to impact, heat, chemicals, and other external factors. It’s non-toxic, which makes it ideal for containers that store food or medication. Its lightweight property makes it an excellent choice for small containers that consumers can carry, such as food packaging.
Polyethylene is a non-hygroscopic material, meaning this plastic resin doesn’t absorb moisture. Instead, water sits on the surface of the material.
It’s possible to modify the properties of HDPE by adding carbon black, a compound that can cancel HDPE’s non-hygroscopic properties if it contains enough oxygen. Carbon black is a common additive for helping HDPE preserve its shape or to protect the material against temperature changes and exposure to light.
What Happened with HDPE Filament?

In spite of its excellent impact resistance and other beneficial properties, HDPE filament isn’t as popular as it used to be. HDPE’s heat resistance emerged as a significant problem for 3D printing projects. This characteristic makes the material versatile and durable, but it also means that HDPE filament has a high melting point.
Since 3D printers have to heat filaments to bend them into the desired shape, it means the 3D printer is using more energy when printing with HDPE filament.
The high melting point also means that the finished product goes through a significant temperature change when it cools down. This thermal shift often results in wrapping and makes it difficult to obtain consistent results in terms of size and shape.
Plus, if the operator doesn’t set the temperature high enough, the HDPE filament will not flow properly and can clog the nozzle.
Another drawback of this material is that HDPE has excellent adhesive properties when in contact with polyethylene, but it doesn’t adhere well to other materials. It’s an issue for 3D printing since the object can shift during printing.
In short, HDPE is suitable for hobbyists and prototypes, but it’s challenging to work with for any kind of large-scale project. The high melting point makes it difficult to obtain consistent results.
Alternatives to HDPE Filament
Currently, the most popular and efficient alternatives to HDPE are as follows.
1. PLA

PLA or polylactic acid quickly emerged as a popular alternative to HDPE. PLA is a biodegradable plastic derived from corn starch or sugar cane. It’s cost-effective, eco-friendly, and has a much lower melting point.
This low melting temperature limits applications in areas that require exposure to heat, but it makes the 3D printing process more manageable. Printing with PLA uses less energy and results in more consistent shapes. The low melting point opens the door to new techniques like lost PLA casting.
2. PETG
Other types of filaments have also gained in popularity. PETG is an excellent option for applications that require a material that resists well to chemicals and impact. PETG also has better adhesion compared to HDPE.
3. ABS

For applications that require a material with good insulation and resistance, ABS is an excellent choice. This material lacks flexibility compared to other plastics, but it’s easier to print with ABS than HDPE.
4. Metal

As 3D printing technology continues to evolve, the metal filament is becoming a viable option for applications that require strength and durability.
How to Print with HDPE Filament

Working with HDPE requires a few adjustments to your printing technique. HDPE has a melting temperature of 230°F, which means you’ll have to set the filament extruder temperature somewhere between 446°F and 500°F or 230 and 260°C.
Be careful not to exceed 500°F since HDPE can release toxic fumes above this temperature.
The density of HDPE filament can vary from one brand to another. You’ll have to adjust the nozzle temperature until you find the ideal melting point. Keep an eye on the filament and look for a temperature that gives you a steady output with a consistent filament thickness.
You’ll need a heated bed to work with HDPE filament. You can set the bed temperature somewhere between 212 and 266°F or 100 to 130°C.
You’ll get better results if you set the printing speed at 20 mm/s. Slow down the printing speed if you run into issues with wrapping or curling.
Due to the high melting point of HDPE filament, you can benefit from working with a cooling fan on the part you’re printing, and it’s also best to use a 3D printer with a closed enclosure for safety reasons.
If you run into issues with poor adhesion to the bed, you can use diluted vinyl glue to prevent the part from shifting. You can also print on a polypropylene mat since HDPE can adhere to this material.
Best Applications for Printing With HDPE
Even though HDPE isn’t as popular as it used to be, this type of 3D printing filament can be a good option for the following projects.
1. Objects With Buoyancy

If buoyancy, or the ability to float in water, is a project requirement for your print, HDPE could be an excellent choice.
This durable material doesn’t absorb water, and its lightweight feel makes it float. It’s also possible to print tight containers and other objects that will use air to flow.
2. Food Storage
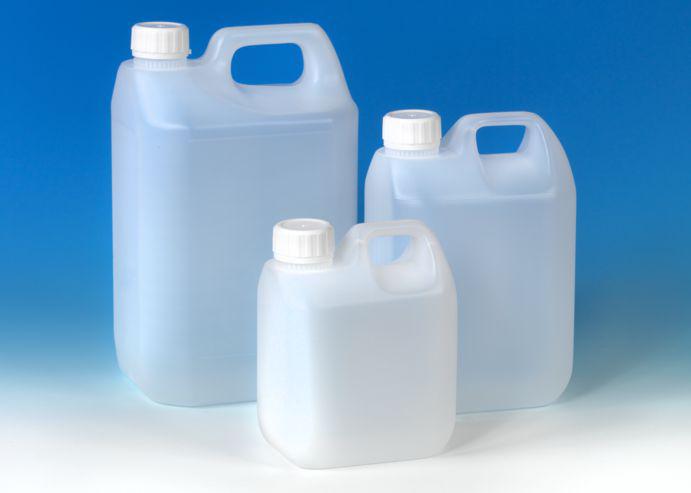

HDPE is a popular material in the food industry. You can find this material in water bottles, food containers, grocery bags, milk jugs, and more.
It’s an excellent choice for a good food container because it’s non-toxic and can protect food from chemicals, humidity, and impact. Plus, its non-hygroscopic properties mean you can use it to store liquids safely.
3. Medical Applications
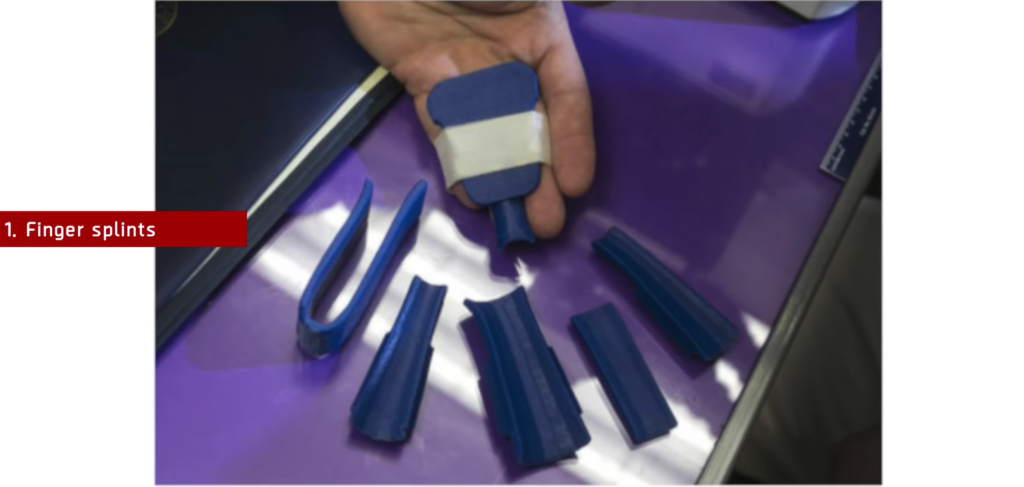

HDPE is a popular material in the healthcare industry. Because it’s flexible and easy to work with, it’s a standard option for customized medical implants.
Some researchers have also developed porous HDPE implants that allow human tissue to attach to the implant and grow. These implants can help with facial and cranial reconstruction, and the lightweight feel of HDPE makes these surgical implants much more comfortable than other materials.
Some industrial medical supply makers have also been experimenting with making invasive medical objects from HDPE.
You can also find PPE made from HDPE since this material is lightweight and doesn’t promote bacterial growth. Many medical containers and other materials are used in the medical field.
It’s also easy to sterilize HDPE since this material resists well to chemicals. Healthcare providers can fix the same HDPE object several times without causing any corrosion or damage.
Advantages and Disadvantages of HDPE Filament
Is HDPE filament a good choice for your 3D printing project? Let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons.
Pros
- HDPE is a resistant and cost-effective material with a wide range of uses.
- It doesn’t absorb water, which is ideal for storing liquids or protecting food from humidity.
- It resists chemicals well, meaning you can easily sanitize an HDPE object.
- HDPE has a unique blend of flexibility and durability.
Cons
- HDPE Filament has a high melting point, which makes it challenging to work with if you’re new to 3D printing.
- Adhesion to the 3D printer bed can be an issue.
- HDPE Filament can warp and curl during the cooling process.
Conclusion
While HDPE Filament remains a popular material for food packaging and medical implants, its use in 3D printing isn’t as common as it used to be. This type of polyethylene has some clear advantages regarding flexibility and durability. Still, its high melting point makes it a challenging material to use for 3D printing due to wrapping and other issues.


