The old rumors about how long 3D printing takes no longer apply! A decade ago, 3D printers were slow and took many hours to print just a small part. But times have changed, and technology, even at the consumer level, has significantly improved.
Today, a small 3D print, like a toy that can fit in your hand, only takes about 2 hours! And smaller models, like a washer or screw, can take as little as 10-20 minutes.
Of course, larger 3D prints still take a long time, and models roughly the size of the shoes on your feet can take anywhere from 10 hours to an entire day (or more).
Want to learn more about how long 3D prints take and what factors play a part in determining the print time? Well then, keep reading!
Table of Contents
How Long Does it Take to 3D Print?
The time a 3D print takes to finish depends on several factors, which we’ll get to later. But we can create broad ranges for the print time based on the model’s size. In the sections below, I’ve answered the question “how long does it take to 3D print” based on what type of model you’re printing.
Miniatures
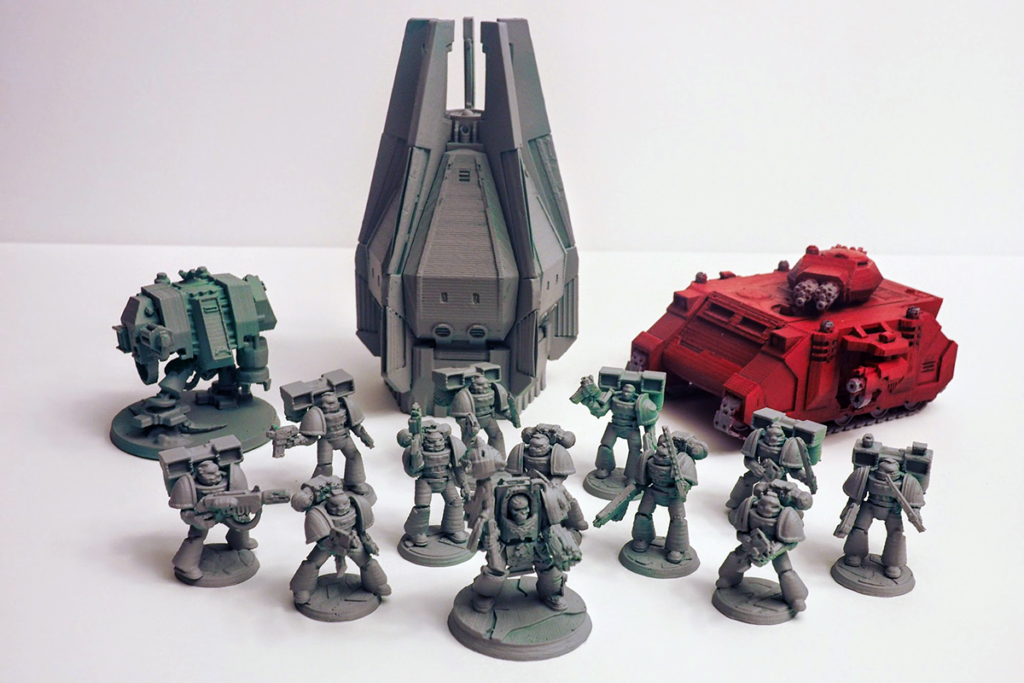

MINIATURES
Miniatures are a class of 3D models that are very small and usually contain a high level of detail. Common examples of miniatures include character figurines from Dungeons & Dragons or Warhammer, and these types of models are super popular for 3D printing on both FDM and resin machines.
But miniatures can also include functional models that are relatively small, such as a cable clip, measuring spoon, or keychain.
For size comparison, a typical miniature 3D model is roughly the same volume as a few LEGO men, and one of these models can easily fit in the palm of your hand. Of course, there’s no hard limit for the size of a miniature, but I like to use 40 x 40 x 40 mm as a maximum volume.
A typical 3D printer, like a Creality Ender 3, can print a miniature 3D model anywhere from 20 minutes to an hour and a half.
The print time for a miniature is usually more dependent on the desired print quality of the model than the volume of the part, which is always very small. That’s because people like to print miniature 3D models slower than average to achieve a higher level of detail on the part.
Regular 3D Models
REGULAR 3D MODELS
Regular 3D models are the next category of 3D prints I’ll be going over, and these are mid-size parts that don’t contain a lot of detail. A regular 3D model is any part that’s not a miniature model and isn’t too large.
While there’s no official maximum size for a regular 3D model, any model more prominent than 40 x 40 x 40 mm but smaller than 100 x 100 x 100 mm would fit in this category. Examples of regular 3D models include a phone holder/stand, vase, toothbrush holder, or laptop stand.
Regular 3D models will take anywhere from 1.5 to 5 hours to print, depending on the printer and the specific model.
Large Prints

LARGE PRINTS
Our last bin of 3D models is large prints. Large prints are relatively significant parts; these models are typically more than 100 x 100 x 100 mm in volume.
Examples of large prints include wall art, a helmet, a giant Christmas tree star, or a mug. Practically, just any model that’s bigger than your typical 3D print!
Large 3D prints are the most extended prints, taking anywhere from 5 hours to over a day to finish.
Check out our related article for the best large format 3D printers here to learn more.
Factors that Affect 3D Printing Time
Many factors go into the estimated time of a print job, from the model’s size to the type of 3D printer used. In the sections below, I’ve gone over the most significant factors that affect the 3D printing time.
3D Model Size
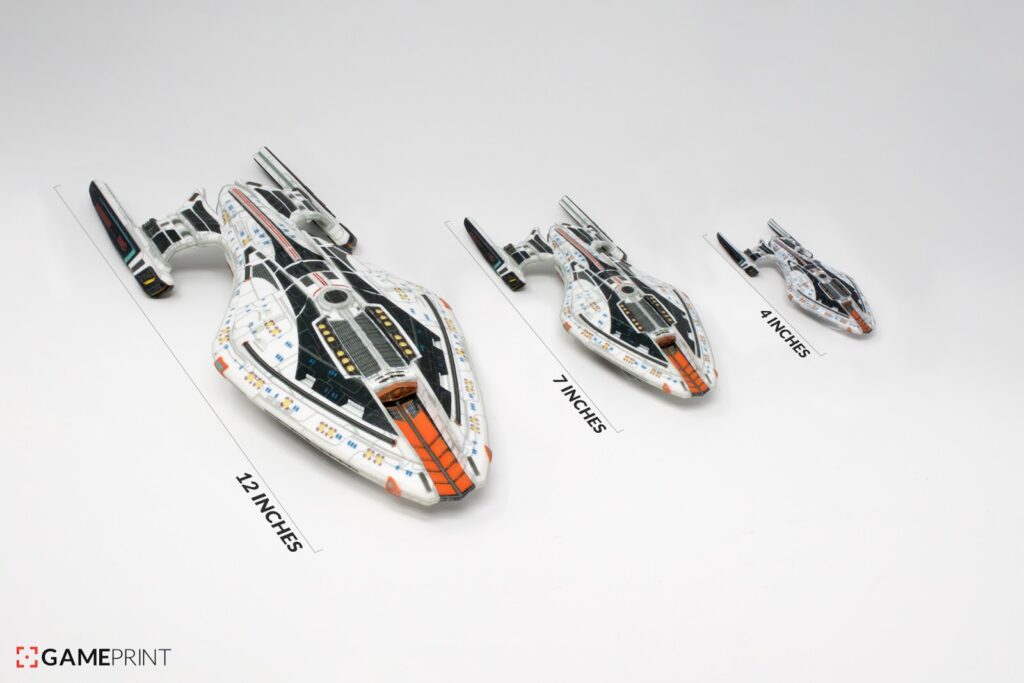

3D MODEL SIZE
The most impactful factor for the print time is the size of the 3D model. As I covered in the previous sections, different sizes of models take significantly different amounts of time to print.
The correlation between the volume of a 3D model and print time is exponential and not linear because 3D models are inherently three-dimensional, so print time increases a lot every time the model size increases.
For example, a typical 100% scale 3DBenchy model takes my printer about 100 minutes (1 hour and 41 minutes) to print. But, if I scale the 3DBenchy to 125%, the new estimated print time is 164 minutes. That’s a 62% increase in print time from just a 25% increase in volume!
Because of this phenomenon, the 3D model size is the most impactful factor regarding the time a print takes.
Layer Height
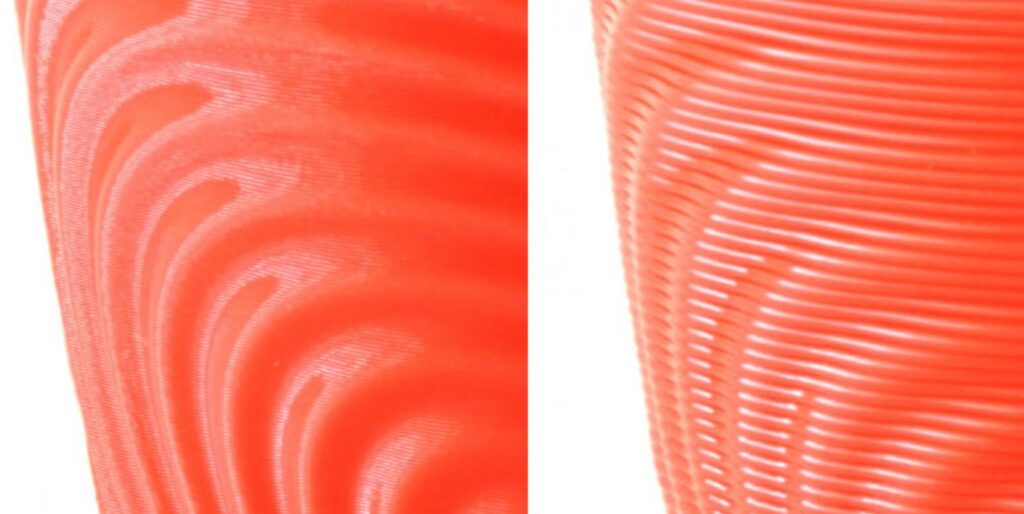

LAYER HEIGHT
Layer height is a 3D slicer setting that controls the spacing between each layer of a 3D print. The larger the layer height, the fewer layers a 3D model will have. And, if a model has fewer layers, the nozzle moves significantly less, greatly affecting the print time.
As such, when the layer height increases, it will significantly lower the print time.
Going back to my 3DBenchy example, if I’m printing the model at scale with a 0.2-mm layer height, the estimated print time is roughly 100 minutes. But, if I change the layer height to 0.24 mm and don’t change any other setting, the new print time is 87 minutes.
It’s not the most significant change, but it’s noticeable.
It’s also worth noting that the layer height’s effect on the print time will exponentially increase with the model’s size. If I were printing the 3DBenchy at 200% scale, the difference between a 0.2 and a 0.24-mm layer height would be almost an hour (55 minutes).
But, a more considerable layer height also affects the level of detail on a print. Furthermore, a smaller layer height means more layers, giving the printer more opportunities to pack pieces and small features into a model. Keep this in mind every time you adjust the layer height!
Shells

SHELLS
Shells on a 3D print include the walls and top and bottom layers of the model. These features are shells (or perimeters) because they separate the model’s internal filling (infill) from the outside of the part.
Shell features are printed completely solid, which can significantly impact how long a print takes. More shells, which means a larger wall thickness and more top and bottom layers, equals a longer print time.
And, like with layer height, the impact that shells (walls, top layers, bottom layers) have on the print time grows exponentially with the volume of the model.
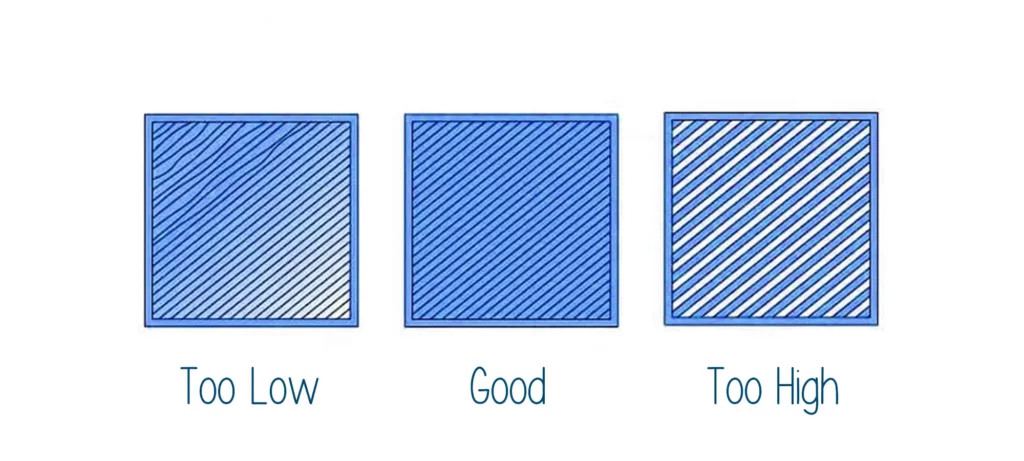
Infill Density

INFILL DENSITY
Infill is the internal filling on a 3D print, trapped between the walls and the top/bottom layers of the model. How solid and whole the infill structure is inside a 3D print is controlled by a slicer setting known as infill density.
Infill density is a percentage, and the higher it is, the more full your 3D model is. The higher the infill density, the longer a print takes and the more substantial (and heavier) it is. For reference, a 100% infill density will yield a solid print, while a 0% infill density would produce a hollow part.
A typical infill density is 20-30%, but you can go even lower to achieve quicker print times.
Print Speed

Print speed determines how fast the nozzle moves and extrudes filament. A higher print speed will lower your print time.
However, with any increase in print speed, it’s essential to increase the nozzle temperature. That’s because if you want to push the filament out of the hot end faster, you’ll need to ensure that it has the heat to melt the plastic fast enough to sustain the print speed. You’ll probably run into under-extrusion or other printing issues if you increase the print speed without expanding the nozzle temperature.
A typical print speed for printing PLA is 45-65 mm/s. But the best print speed depends on what 3D printer you have and a few other factors. Check out our article on the most optimal print speed settings here to learn more.
3D Printing Technology

The 3D printing technology also matters for how fast prints are made. Today, there are tens of different printing technologies, but the two most common ones for consumer-grade 3D printing are FDM and SLA (resin).
FDM 3D printers include machines like the Creality Ender 3 and Elegoo Neptune 3 that heat filament and push it through a nozzle to make a part, layer by layer. On the other hand, resin 3D printers use high-precision lasers and mirrors to solidify liquid resin layer-by-layer to create the desired 3D model.
In general, FDM 3D printers are faster than SLA machines. However, the difference in print time between the two technologies is slight, and SLA technology is quickly improving, so SLA machines might even be faster than FDM printers within the next few years.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that resin 3D printers yield much better-looking 3D prints, with practically invisible layer lines and a high level of detail.
Complexity of 3D Model
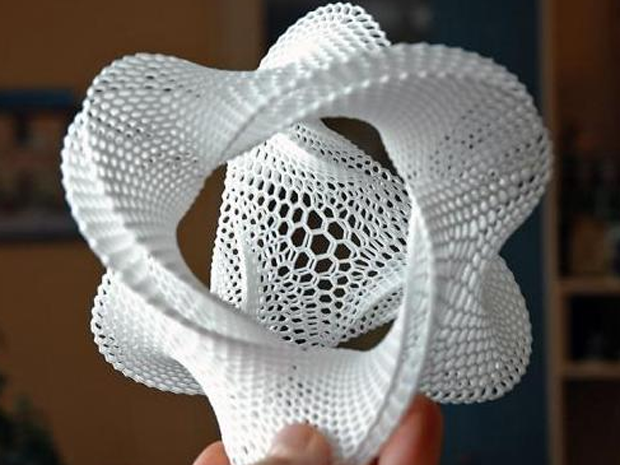

COMPLEXITY OF 3D MODEL
The complexity of your 3D model also matters a lot in how long it takes. While it’s not a direct effect, if your model is more complex (contains more detail and minor features), you’ll be forced to use specific slicer settings that lead to a longer print time.
For example, if you are printing a high-detail model, you’ll want to use a slower print speed and a smaller layer height to ensure the parts come out nice. Both of these slicer settings changes increase the print time!
Ways to Speed Up Your 3D Printer
There are a handful of ways to speed up your 3D printer if you want to print faster. In the sections below, I’ve gone over some of the most effective methods:
Lower Infill Density
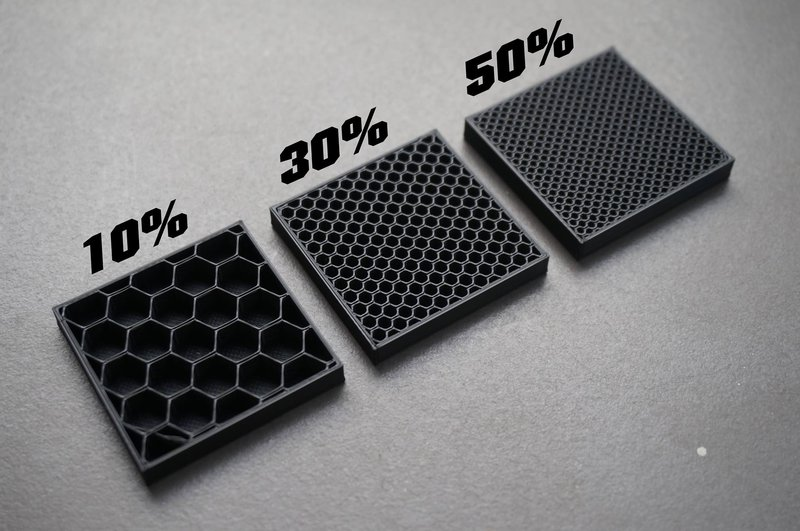
First, you can lower the infill density for your print for a sure-fire way to reduce the print time. As I explained previously, the infill density is the percentage of how complete the inside of your 3D print is.
Lowering this percentage means less filament is laid down to make your print and the nozzle has to move around less, so the print time is lower.
Raise Layer Height
Second, you should raise the layer height, as this will drop the print time by a good bit, especially if you’re printing a large model.
The maximum layer height you can use with a 0.4 mm nozzle (most nozzles) is about 0.28 or 0.3 mm. But you don’t have to use a layer height that high.
Instead, I’d recommend going up to 0.2 mm for the layer height if you use something smaller. And, if you’re already using a 0.2 mm layer height and want to speed up your printer further, try going to 0.24 mm.
Use a Wider Nozzle Diameter

Next, using a wider nozzle diameter will enable you to print faster. As I mentioned in the previous section, what layer height you can use is determined by your nozzle diameter. Using a wider nozzle will allow you to successfully use more enormous layer heights, which will, in turn, lower your print time.
If you’re using a 0.4 mm nozzle, consider switching to a 0.6 or 0.8 mm nozzle. Doing so will allow you to use a layer height as higher as 0.6 mm, significantly lowering your print time by several hours.
Increase Print Speed
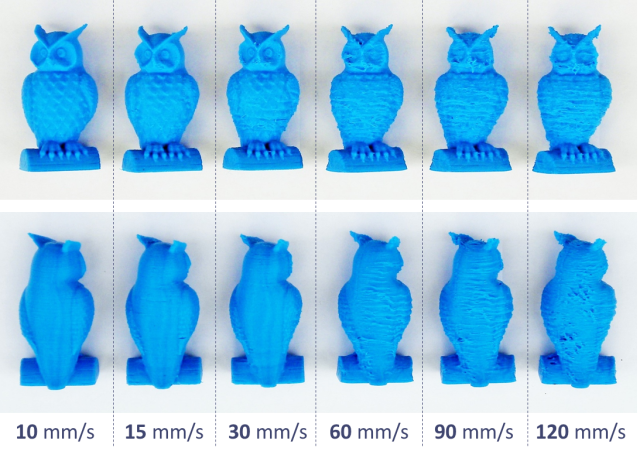
Finally, as you probably guessed, increasing your print speed will lower your print time.
Of course, you want to use a reasonable print speed, as this will likely cause issues with your print quality. However, increasing your current printing speed by 5, 10, or even 15 mm/s might be possible and will lower your print time.
For PLA, consider using a speed of 60 mm/s if you’re not doing so already. And, if you are, then try 65, 70, or even 75 mm/s. Just make sure to also increase your nozzle temperature accordingly.
What Happens if You 3D Print Too Fast?
3D printing too fast, whether on an FDM or SLA machine, is likely to lead to a low-quality print. Moreover, if you don’t give each layer of your print enough time to properly cool down and cure before the next layer comes down, your print will likely contain many defects and imperfections, like blobs or zits.
Additionally, printing too fast increases the chances of under-extrusion, one of the most notorious problems with 3D printers. Under-extrusion can cause gaps in your prints or, in severe cases, lead to complete print failures.
Is it Faster to 3D Print Multiple Objects at Once?
No!
Despite what you might think, printing multiple objects simultaneously is slower than printing them one at a time.
The reason for this is travel moves. Moreover, because 3D printers make parts layer-by-layer, the nozzle has to travel between each component at every layer if you print multiple pieces at once. This travel time adds up quickly and makes multi-object print jobs take much longer than simply printing parts one after the other.
Additionally, printing multiple objects leads to lower-quality prints than printing them individually. That’s because the travel moves in printing numerous parts can cause more printing defects, like blobs, to appear on the prints.
Conclusion
While 3D printing may seem super slow, it’s not called “rapid prototyping” for no reason. The technology makes producing custom-designed parts much faster than traditional manufacturing methods, like injection molding. And, over the past decade, 3D printing has gotten significantly more quickly.
Today, in under an hour, you can print a miniature model, like a little character figurine or a screw. As for mid-size models, like a phone stand, you can expect a print time between 1.5 to 5 hours.
Finally, large models take the most time to print and by a lot. A typical sizable 3D print, like a shoe or a big trophy, can take anywhere from 5 hours to over a day. But, still, compared to traditional manufacturing for custom parts, this is a short time.
And there are many ways you can speed up the printing process. For example, increasing the printing speed and layer height can cut the print time by several hours.
Enjoy!